Shockwave therapy (ESWT) is a non-invasive treatment that uses high-energy acoustic waves to promote healing and relieve pain. Originally developed to break up kidney stones, it is now widely used for musculoskeletal conditions. Here’s what you need to know:
- How It Works: The therapy stimulates tissue repair, improves blood flow, and reduces pain by triggering cellular responses like ATP production and anti-inflammatory changes.
- Conditions Treated: Common uses include plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendinopathy, calcific shoulder tendonitis, and chronic pain conditions like tendinopathies.
- Types of Therapy:
- Radial: Targets surface-level tissues, ideal for broader areas.
- Focused: Penetrates deeper tissues for precise treatment.
- Success Rates: Studies show 60%–91% effectiveness for tendinopathies, with plantar fasciitis and calcific tendonitis showing the best outcomes.
- Treatment Details: Sessions last 10–30 minutes, with most patients needing 3–6 sessions spaced a week apart.
Whether you’re dealing with chronic pain or a specific injury, shockwave therapy offers a targeted approach to healing without surgery or medication.
The Science Behind Shockwave Therapy
How Sound Waves Promote Healing
Shockwave therapy relies on acoustic waves to jumpstart physical and biological healing in tissues. These waves have two distinct phases: a high-pressure phase, which can peak at up to 100 MPa in less than 10 nanoseconds, and a subsequent tensile phase [2]. When these waves interact with damaged tissues, they initiate a process called mechanotransduction, which involves cavitation and cellular responses.
Here’s how it works: the acoustic waves generate tiny bubbles within the tissue. When these bubbles collapse, they produce secondary shockwaves and microjets, which help deliver healing molecules to the injured area. This cavitation effect activates mechanoreceptors, including extracellular matrix proteins, stretch-activated ion channels, cell–cell junction receptors, and cytoskeletal components [2]. These cellular changes lead to increased ATP production, providing the energy necessary for tissue repair. Additionally, the therapy improves local blood flow, further aiding the healing process [1].
But shockwave therapy isn’t just about speeding up tissue repair – it also has a significant impact on pain relief.
How It Eases Pain
Shockwave therapy reduces pain through two primary mechanisms. The first involves the degeneration of small sensory nerve fibers, which decreases the release of pro-inflammatory mediators [1]. The second mechanism, known as hyperstimulation analgesia, activates the body’s natural pain relief systems. This includes the release of endorphins, stimulation of descending pain-control pathways, and a shift in macrophages from a pro-inflammatory (M1) state to an anti-inflammatory (M2) state [1]. Together, these processes enhance recovery and pain management.
Using the maximum tolerable energy density can amplify these pain-relieving effects. Shockwave therapy may also increase the production of lubricin, a molecule that reduces friction and protects tissues [1]. Research by Wang CJ et al. highlights that the therapy boosts growth factors like eNOS, VEGF, and BMP-2 at injury sites [1]. These molecular changes help explain the reported success rates of 60% to 80% for treating various tendinopathies with shockwave therapy [1].
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy: Evolution, Mechanisms, and Clinical Efficacy
Medical Conditions Treated
Shockwave therapy taps into the body’s natural cellular responses to address a variety of musculoskeletal conditions. Here’s a closer look at how it helps with specific areas and chronic issues.
Foot and Leg Problems
Plantar fasciitis is a common condition, affecting about 10% of the population and accounting for 11–15% of all foot pain cases [3]. Similarly, Achilles tendinopathy is another frequent issue, making up nearly 9% of general sports injuries and as much as 18% of running-related injuries. Interestingly, this condition doesn’t just affect athletes – about one-third of cases are seen in non-athletes as well [4].
Arm and Shoulder Problems
Shockwave therapy has shown promising results in treating arm and shoulder ailments, particularly those involving calcification and chronic inflammation. For instance, a study involving 90 patients with calcific tendonitis revealed that 86.6% experienced complete resolution of calcifications, while the remaining participants saw partial improvement [5].
“Shockwave therapy has gained popularity for treating various musculoskeletal conditions, including shoulder tendonitis. This treatment uses pressure waves to stimulate healing within the affected tendons. It not only helps in breaking down scar tissue but also enhances blood flow to the area, promoting faster recovery.” – Glenn Akins, Redwood Orthopaedic Surgery Associates [6]
These benefits make shockwave therapy a valuable option for addressing localized issues and managing chronic pain.
Long-term Pain Conditions
For those dealing with chronic pain lasting three months or more, shockwave therapy offers a practical solution through its ability to modulate pain and stimulate healing [7]. Here’s how it performs across different conditions:
| Condition Type | Success Rate | Notable Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Calcific Tendinitis | 47% at 1-year follow-up | Complete elimination of calcification |
| Plantar Fasciitis | High effectiveness | Significant pain relief and better mobility |
| Patellar Tendinopathy | Positive results | Improved healing and functionality |
| Chronic Tendinopathies | Variable success | Best results when paired with other therapies |
The therapy tends to yield the best results in chronic conditions rather than acute ones [7], especially when it’s part of a broader treatment plan. Its combination of pain relief and healing stimulation makes it a go-to option for many long-term issues.
Shockwave Equipment Types
To understand how shockwave therapy works, it’s essential to know about the equipment used and how it delivers energy to treat various conditions. The therapy relies on two main delivery methods, each designed to target specific tissue depths effectively.
Focused vs. Radial Treatment
There are two types of shockwave treatments: focused and radial. Focused shockwave therapy delivers concentrated energy to deeper tissues, while radial shockwave therapy disperses energy over a wider, more superficial area.
| Feature | Radial Shockwave | Focused Shockwave |
|---|---|---|
| Depth Range | 1.2–1.6 inches (superficial) | Up to 4.7 inches (deep) |
| Wave Speed | 32.8 ft/s | 4,921 ft/s |
| Treatment Area | Large, dispersed | Small, precise |
| Session Requirements | 3–10 sessions | Fewer sessions |
| Pain Level | Higher initial discomfort | More comfortable |
Machine Types and Uses
Shockwave therapy machines use different technologies to generate therapeutic waves, each suited for specific treatment needs. These systems include pneumatic, electromagnetic, and electroacoustic mechanisms, offering flexibility for both superficial and deep tissue treatments.
- Radial systems rely on pneumatic (compressed air) technology. They are ideal for treating surface-level conditions like plantar fasciitis, where the energy spreads out and dissipates as it penetrates deeper.
- Focused systems are designed to maintain energy intensity at greater depths, making them perfect for precise, deep-tissue treatments.
For instance, the Storz system provides a variety of transmitters, enabling practitioners to treat both localized areas and larger, superficial regions effectively [9].
“As a combination therapy, focused shockwave with radial is providing my patients with outstanding results.”
– Helen How, How Clinic Edinburgh [8]
sbb-itb-ed556b0
Treatment Process Guide
Treatment Length and Frequency
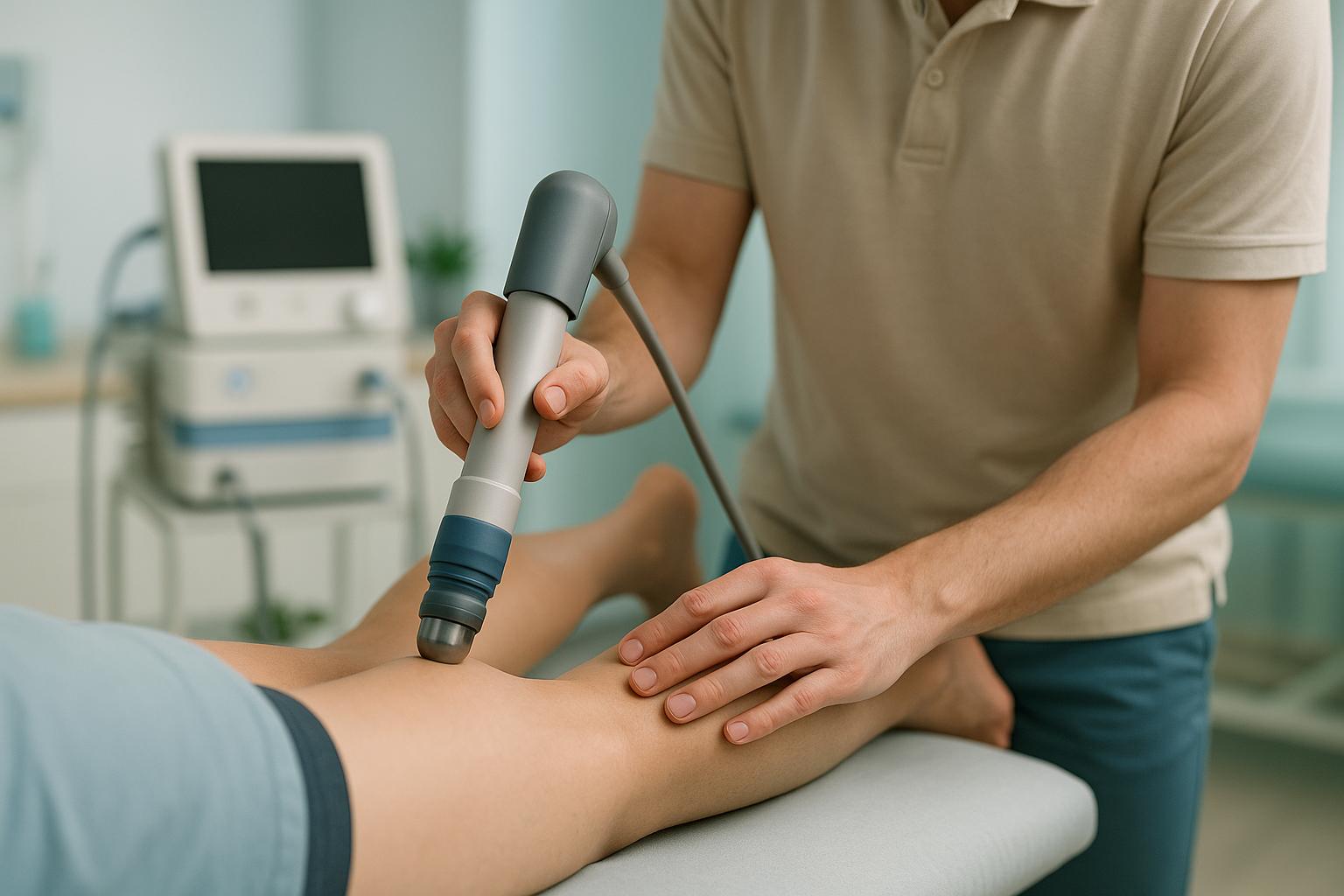
A typical shockwave therapy session runs between 10 and 30 minutes [12]. During your appointment, here’s what to expect:
- Medical Review: Your therapist will go over your medical history and pinpoint the area causing pain [10].
- Comfortable Positioning: You’ll be positioned either sitting or lying down, ensuring you’re relaxed [10].
- Gel Application: Ultrasound gel is applied to the treatment area for effective transmission of the shock waves [10][11].
- Shockwave Delivery: Using a handheld probe, the therapist administers about 1,500 to 2,000 shock waves [10].
Most patients need 3 to 6 sessions, spaced about a week apart, to achieve the best outcomes [12].
| Treatment Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Session Duration | 10–30 minutes |
| Number of Sessions | 3–6 treatments |
| Time Between Sessions | 7–10 days (weekly intervals) |
| Shock Waves per Session | 1,500–2,000 |
Proper recovery and aftercare following each session play a key role in maximizing the benefits [13].
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery and aftercare are crucial for getting the most out of your treatment. You’ll typically notice the full effects of the therapy within 4 to 7 days [13]. Here’s how to manage recovery:
Immediate Aftercare (First 48 Hours)
- Skip NSAIDs and Ice: Avoid anti-inflammatory medications and ice packs [13].
- Pain Management: If needed, opt for over-the-counter Tylenol [13].
- Stay Hydrated and Rested: Drink plenty of water and aim for 8–9 hours of sleep [13].
- Limit High-Impact Activities: Avoid intense exercises during this period [14].
Extended Recovery Period
- Mild Discomfort: It’s normal to feel slight soreness or stiffness for 2–3 days after treatment [13].
- Nighttime Sensations: Some people experience mild “shooting pain” at night as part of the healing process [13].
- Activity Restrictions: Refrain from heavy physical activities for about 4 weeks to aid recovery [15].
Nutrition and Lifestyle Tips
- Eat Well: Focus on a diet rich in protein, fruits, and vegetables [13].
- Cut Back on Sugars and Alcohol: Reducing processed sugars and alcohol can support healing [13].
- Topical Comfort: Use magnesium cream or lidocaine if needed for localized relief [13].
- Gentle Movement: Incorporate light stretching and use warm compresses as advised [14].
These steps not only help with recovery but also enhance the overall effectiveness of the treatment.
Results and Safety Information
Success Rates by Condition
The effectiveness of shockwave therapy depends on the condition being treated, with an overall satisfaction rate of about 80% [21].
Here’s a quick look at treatment outcomes based on recent meta-analyses:
| Condition | Short-term Results | Evidence Quality | Treatment Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plantar Fasciitis | Noticeable improvement in pain and function | High | Strong positive effect |
| Patellar Tendinopathy | Minimal improvement compared to placebo | Low–Moderate | Negligible effect |
| Achilles Tendinopathy | Slight improvement in pain | Low | Inconclusive effect |
For most conditions, the best results tend to surface 8–12 weeks after treatment [21]. Among these, plantar fasciitis shows the most promising outcomes, with high-quality evidence confirming significant reductions in pain and improvements in function [16].
“As a manual treatment, it may take some time for the results of Shockwave Therapy to become apparent.” – The Guyer Institute of Molecular Medicine [21]
These findings highlight the therapy’s potential, setting the stage for a closer look at its safety aspects.
Risk Factors and Limitations
While the benefits of shockwave therapy are compelling, understanding its safety profile is essential for managing expectations. The treatment is generally safe but can cause temporary discomfort and is not suitable for everyone [17][18].
Common Side Effects
Patients may experience mild, temporary side effects such as:
When Shockwave Therapy Is Not Recommended
Certain conditions make this treatment unsuitable, including:
- Pregnancy
- Recent post surgical at the treatment site
- Bleeding disorders
- Active cancer at the treatment site
- Presence of pacemakers [17][19][20]
To reduce risks, consider the following:
- Seek treatment from qualified professionals
- Share all relevant medical history and medications
- Follow pre- and post-treatment instructions carefully
- Report any unusual symptoms immediately [18][19]
Treatment outcomes can also vary based on factors like the patient’s age, the location of the injury, and their sensitivity to pain [22]. Although rare, serious complications such as skin burns, nerve damage, or tissue injury can occur, underscoring the importance of proper techniques and equipment calibration [18].
Making Your Treatment Decision
When considering shockwave therapy, it’s important to weigh its reported success rates and safety profile alongside your specific needs and health condition.
Shockwave therapy is often used to treat soft tissue injuries and musculoskeletal issues, including:
- Plantar fasciitis and heel spurs
- Calcific shoulder tendinosis
- Patellar tendonitis
- Lateral and medial epicondylitis (commonly known as tennis or golfer’s elbow)
- Chronic tendinopathy
Practical Treatment Details
Here are some logistical aspects to consider before starting therapy:
| Aspect | Details | Things to Keep in Mind |
|---|---|---|
| Session Duration | 15–30 minutes | Plan for regular appointments. |
| Treatment Course | 3–10 sessions | The number of sessions depends on the severity of your condition. |
| Type Options | Radial or Focused therapy | Focused therapy penetrates deeper tissues. |
These factors, combined with clinical evidence, can guide your decision. Research indicates that shockwave therapy stimulates the body’s natural healing processes, potentially reducing the need for surgery or long-term medication use [24].
Important Health Considerations
Before starting treatment, be aware of the following contraindications [25]:
- Pregnancy
- Blood clotting disorders
- Recent steroid injections (within the past 6 weeks)
- Presence of a pacemaker
- Active infection at the treatment site
Steps to Make an Informed Decision
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Discuss your complete medical history and any current medications with your provider to ensure shockwave therapy is a safe option for you [25][26]. - Check Insurance Coverage
Verify whether shockwave therapy is covered under your insurance plan [24]. - Explore Alternatives
Compare shockwave therapy with other treatment options, such as injections or surgery, particularly for conditions like calcific shoulder tendinosis [23].
For many, combining shockwave therapy with exercises and other physical treatments can further enhance results [23]. Work with your healthcare provider to create a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
FAQs
What are the possible side effects of shockwave therapy, and how can they be managed?
Shockwave therapy is considered safe for most people, though temporary side effects like mild pain, swelling, or bruising around the treatment area can occur. The good news? These symptoms usually fade on their own within a few days.
If discomfort arises, try using a cold pack on the area or consider taking an over-the-counter pain reliever, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. However, if the pain gets worse, lingers, or if you notice anything unusual, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for advice and further evaluation.
While severe side effects are extremely uncommon, keeping an open line of communication with your provider ensures you receive the best care and can recover with confidence.
How does shockwave therapy compare to other treatments for chronic pain and musculoskeletal issues?
Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive and drug-free option that uses high-energy sound waves to encourage healing and reduce pain. Unlike medications that often just cover up symptoms, this therapy works by addressing the underlying issue – stimulating tissue repair and improving blood circulation. This can lead to longer-lasting relief without the side effects typically linked to pharmaceuticals.
While treatments like physical therapy or chiropractic care can also be helpful, shockwave therapy stands out for its effectiveness in treating conditions such as plantar fasciitis, tendinopathies, and musculoskeletal injuries. The right treatment depends on your specific condition, overall health, and what you’re comfortable with. Be sure to consult your healthcare provider to see if shockwave therapy could be a good fit for you.
Is shockwave therapy right for everyone, and what conditions might make it unsuitable?
Shockwave therapy is considered a safe option for many, but it isn’t the right fit for everyone. There are specific cases where it’s not recommended, such as during pregnancy, for individuals with bleeding disorders, or if there’s cancer in or near the area being treated. Additionally, having a pacemaker, an active infection, or recent corticosteroid injections in the treatment zone are other factors that might rule out this therapy.
If you have any health conditions or are on medication, it’s crucial to talk with your healthcare provider beforehand. They can assess your situation and decide if shockwave therapy is a suitable and safe choice for you.


No responses yet