Two treatments stand out for managing patellar tendinopathy: Fascial Manipulation® and eccentric training with static stretching. Here’s what you need to know:
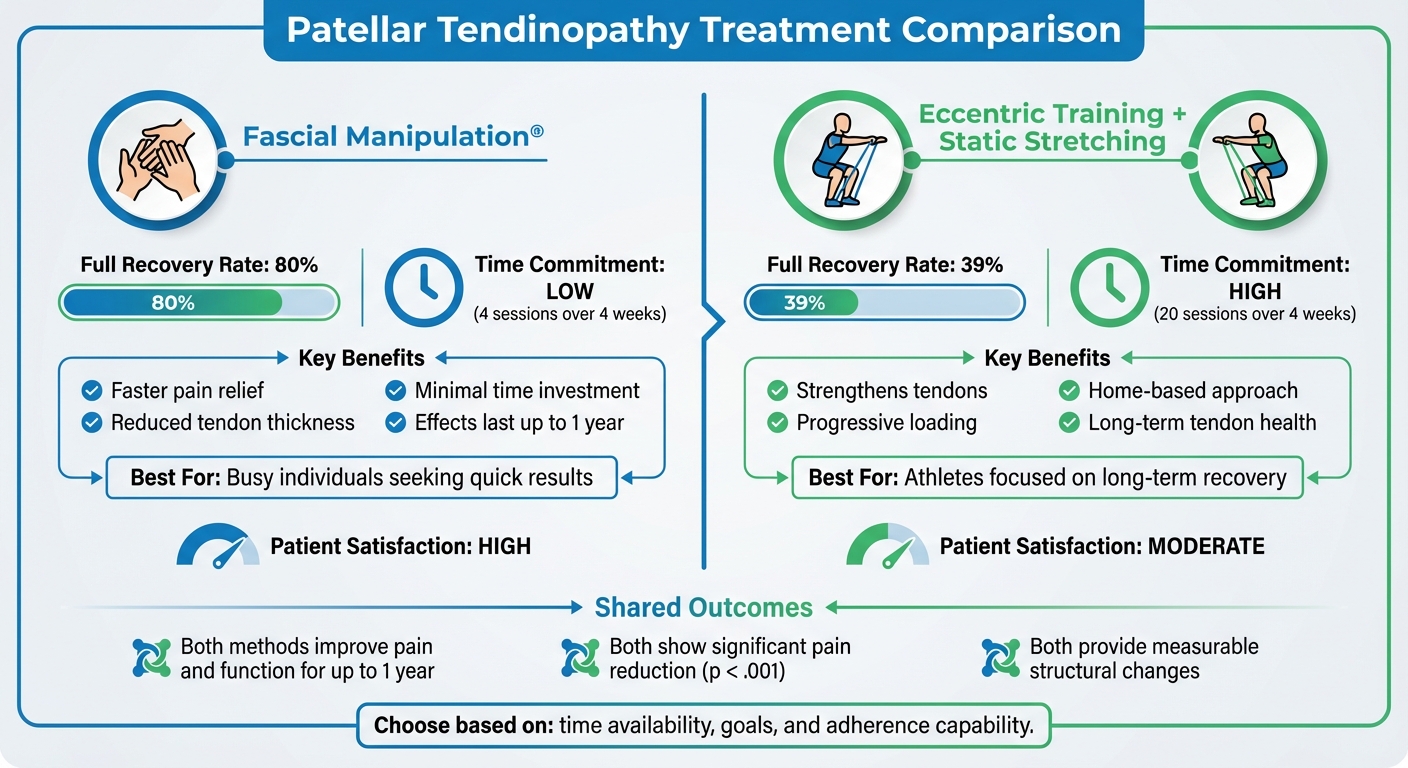
- Fascial Manipulation®: Involves four weekly sessions of targeted manual therapy. 80% of patients reported full recovery. Benefits include reduced pain and tendon thickness, with effects lasting up to a year.
- Eccentric Training + Static Stretching: Requires 20 sessions over four weeks (5 sessions/week). 39% of patients achieved full recovery. This method improves tendon strength but demands more time and effort.
Key Findings:
- Both methods improve pain and function for up to a year.
- Fascial Manipulation® is less time-intensive, with higher patient satisfaction.
- Eccentric training suits those focused on tendon strength and long-term health.
Quick Comparison:
| Treatment Method | Sessions Required | Full Recovery Rate | Key Benefit | Patient Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fascial Manipulation® | 4 weekly | 80% | Faster relief with fewer sessions | Busy individuals, quick results |
| Eccentric + Static Stretch | 20 (5/week) | 39% | Strengthens tendons | Athletes, long-term focus |
Choosing the right treatment depends on your time, goals, and ability to stick to a routine.
Fascial Manipulation vs Eccentric Training for Patellar Tendinopathy: Treatment Comparison
Patellar Tendinopathy / Tendinitis / Tendinosis | Jumper’s Knee Rehab (Education, Myths, Exercises)
sbb-itb-ed556b0
1. Fascial Manipulation®
Fascial Manipulation® works by applying manual pressure to the quadriceps, which helps warm up the fascial tissue. This increase in temperature softens the fascia, changing it from an abnormally dense state to a more fluid, flexible condition. This change restores the natural movement between connective-tissue layers and allows intrafascial nerve endings to move more freely, contributing to its ability to relieve pain. This improved mobility is a key factor behind the significant pain relief observed in clinical studies [2].
Clinical trials have shown that this method delivers results with minimal time investment. Patients underwent just four one-hour sessions over the course of a month. According to lead author Rajasekar Sannasi, Fascial Manipulation® not only requires fewer sessions but also achieves high levels of patient satisfaction when compared to eccentric training approaches [1].
What’s even more impressive is that a single session of targeted manipulation provided immediate pain relief. These effects lasted for at least one month, showcasing how the short-term benefits of Fascial Manipulation® can translate into longer-term improvements [1].
The treatment also brought about measurable structural changes that go hand-in-hand with its rapid pain relief and lasting functional improvements. During the first month, ultrasound imaging showed a reduction in the thickness of the hypoechoic area of the patellar tendon. Follow-up data confirmed that the pain relief and functional improvements remained consistent for at least one year [1].
For individuals who struggle with sticking to daily exercise routines, Fascial Manipulation® offers a practical and efficient alternative. With just four sessions, this technique delivers functional results that are comparable to – or even better than – more time-intensive methods. This makes it an especially appealing option for athletes and active individuals looking to maintain their performance without a heavy time commitment.
2. Eccentric Training with Static Stretching
Eccentric training paired with static stretching is a well-established method for addressing patellar tendinopathy. This treatment typically involves exercises like decline squats performed on a 25° incline, combined with 30-second static stretches for the quadriceps and hamstrings before and after each session[4].
Unlike the quicker intervention of Fascial Manipulation®, this approach follows a much more demanding schedule. Patients are required to complete 20 sessions over four weeks, exercising five times per week[1]. A randomized clinical trial conducted between August 2019 and December 2020 in an outpatient physiotherapy clinic in India highlighted its effectiveness. Patients adhering to this protocol saw notable improvements in their VISA-P scores, gaining 14 points by the end of the treatment and 19 points at the six-month follow-up compared to those who only practiced eccentric training[4]. This structured and intensive routine stands in stark contrast to the minimal session requirements of Fascial Manipulation®.
"Eccentric training combined with static stretching is superior to eccentric training alone to reduce pain and improve function in patients with patellar tendinopathy at the end of the treatment and at follow-up." – Dimitrios Stasinopoulos, PhD, Clinical Rehabilitation[4]
While the results in terms of pain reduction (p < .001) and VISA-P score improvements were significant and sustained even at the one-year mark, patient satisfaction told a different story. Only 39% of participants in the eccentric training and stretching group reported complete recovery on a six-point Likert scale[1]. This contrast highlights the challenge of adhering to such an intensive regimen, even when the benefits are evident.
The success of this protocol lies in its focus on progressive loading, which promotes tendon adaptation. Patients are instructed to perform three sets of 15 repetitions, maintaining pain levels at a manageable 5/10 threshold[3][5]. While this structured approach delivers meaningful improvements, the commitment it demands – 20 sessions over four weeks – may deter some patients, especially when less time-intensive alternatives offer similar outcomes. In short, while effective, the rigorous nature of this treatment may pose challenges for adherence.
Advantages and Disadvantages
When comparing the treatment methods outlined earlier, it’s clear that each comes with its own strengths and challenges. According to the clinical trial, both approaches provide noticeable pain relief and improved functionality for up to a year [1].
Fascial Manipulation® is particularly appealing for its time efficiency. With just four weekly sessions, it delivers results that match – or even surpass – those of the more intensive 20-session protocol. Its hands-on approach tends to enhance patient satisfaction, as shown by the higher recovery rates mentioned earlier [1].
On the other hand, the eccentric training with static stretching method presents a more active and involved process. It requires a commitment to 20 sessions over four weeks, with exercises performed five times a week. This home-based plan is especially beneficial for athletes aiming to rebuild their tendons and return to sports, as it aligns with established tendon remodeling techniques [1].
Choosing between these two methods often comes down to personal preferences and treatment goals. Fascial Manipulation® is ideal for those looking for quick pain relief with minimal time investment, making it a practical option for patients juggling busy schedules. Meanwhile, eccentric training with static stretching may resonate more with individuals who prefer a self-directed approach and are focused on achieving long-term tendon health [1].
Conclusion
This randomized clinical trial sheds light on effective strategies for managing patellar tendinopathy. Both Fascial Manipulation® (FM) and eccentric training showed significant improvements in pain and function over the course of a year. However, FM stood out with an 80% recovery rate achieved in just four sessions, compared to a 39% recovery rate requiring 20 sessions for eccentric training [1]. These results highlight the importance of tailoring treatment approaches to the specific needs of each patient.
While both treatments delivered positive outcomes, FM offered the added benefit of requiring fewer sessions, which also translated to higher patient satisfaction [1]. For healthcare providers, this makes FM a strong contender as a primary treatment option, particularly for individuals who may find frequent exercise protocols challenging to maintain. FM’s ability to deliver quicker pain relief with fewer visits makes it an appealing choice for patients seeking a more time-efficient solution [1].
That said, patient selection plays a crucial role. FM may be ideal for those with demanding schedules or difficulties adhering to home-based exercise regimens. On the other hand, eccentric training, paired with static stretching of the quadriceps and hamstrings, remains a valuable option – especially for athletes aiming for long-term tendon health and a safe return to sports [1].
Ultimately, choosing the right treatment requires considering the patient’s lifestyle, treatment goals, and adherence capabilities. Both approaches have proven their effectiveness, making it essential to align the chosen method with the individual’s unique circumstances.
FAQs
What are the long-term benefits of Fascial Manipulation® compared to eccentric training with static stretching for patellar tendinopathy?
Fascial Manipulation® has demonstrated extended pain relief and notable functional improvements when compared to a combination of eccentric training and static stretching. On top of that, it often requires fewer treatment sessions, making it a practical and time-efficient choice for managing patellar tendinopathy.
This method works by addressing the underlying causes of pain, focusing on fascial imbalances. By targeting these issues directly, it aims to deliver results that are more enduring. Clinical findings suggest that for those looking for effective, lasting relief, Fascial Manipulation® could be a highly effective option.
Which treatment is more effective for patellar tendinopathy: Fascial Manipulation® or eccentric training with stretching?
Fascial Manipulation® often leads to quicker recovery for patellar tendinopathy, typically requiring fewer treatment sessions than combining eccentric training with static stretching. This method targets fascial imbalances, helping to alleviate pain and restore function more efficiently.
Both approaches can be effective, but the right choice depends on your specific needs and circumstances. It’s always a good idea to consult a healthcare professional to decide which treatment is best suited for your recovery.
When might eccentric training be a better choice than Fascial Manipulation® for managing patellar tendinopathy?
Eccentric training could be a great fit for people who prefer taking charge of their recovery through a structured, exercise-focused plan. This approach works particularly well if you have access to a physical therapist but want to reduce the number of in-person therapy sessions.
If you’re someone who enjoys being actively involved in your recovery and doesn’t mind committing to a guided exercise routine, eccentric training might align perfectly with your needs and lifestyle.
Related Blog Posts
- What Conditions are Dry Needling Beneficial For?
- Effectiveness of Articular and Neural Mobilization for Managing Cervical Radicular Pain: A Systematic Review With Network Meta-Analysis
- Cost-effectiveness of spinal manipulation, exercise, and self-management for spinal pain
- Tendinopathy: The Interplay between Mechanical Stress, Inflammation, and Vascularity



Comments are closed