Neuroimmune interactions explain how the nervous and immune systems communicate to manage pain, inflammation, and healing. When this system is disrupted, it can lead to chronic pain and slower recovery in conditions like arthritis, chronic back pain, and fibromyalgia. Here’s what you need to know:
- What happens: Nerves and immune cells exchange signals using molecules like neurotransmitters and cytokines. This effects pain perception and inflammation.
- Why it matters: Dysregulated neuroimmune responses can amplify pain and prolong inflammation, making recovery harder.
- Conditions impacted: Chronic back pain, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoarthritis are examples where neuroimmune dysfunction plays a role.
- Treatment options: Chiropractic care, dry needling, and shockwave therapy are some methods that target neuroimmune pathways. Lifestyle changes like exercise and an anti-inflammatory diet also help.
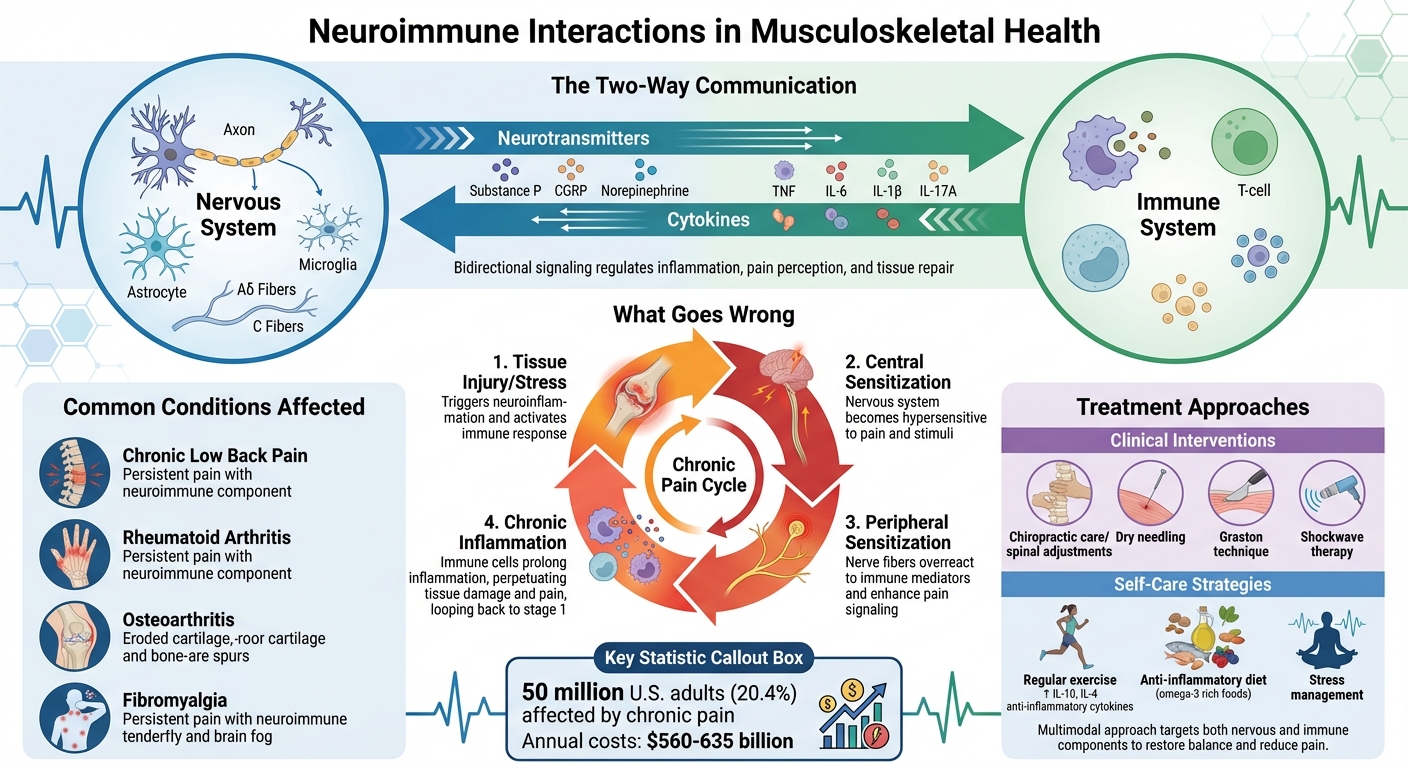
How Neuroimmune Interactions Affect Musculoskeletal Pain and Inflammation
How Neuroimmune Pathways Affect Musculoskeletal Conditions
Key Neuroimmune Mechanisms
The interaction between nerves and immune cells plays a crucial role in musculoskeletal health. When tissues are injured or under stress, neuroinflammation occurs. In this process, glial cells like microglia and astrocytes release proinflammatory molecules, triggering a cascade of events that lead to central sensitization. This means the nervous system becomes more sensitive to pain signals, while also attracting peripheral immune cells, which can prolong inflammation [4][3][6].
Peripheral sensitization happens when nerve fibers, specifically Aδ and C fibers, become overly sensitive after exposure to immune mediators like TNF, IL-6, IL-1β, IL-17A, and substances such as histamine and NGF. These immune signals amplify pain perception, making even minor stimuli feel more intense.
The nervous system also actively influences immune responses. It does this by releasing molecules like Substance P, CGRP, and norepinephrine, which bind to receptors on immune cells [1]. This creates a two-way communication system where the nervous system can adjust immune activity. For example, in joint disorders like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, macrophages are especially important. These immune cells are highly responsive to neurotransmitters, which makes them key players in the nervous system’s ability to regulate inflammation.
These mechanisms form the foundation for understanding how chronic musculoskeletal conditions develop and persist.
Common Conditions Affected by Neuroimmune Interactions
Some musculoskeletal conditions clearly illustrate the impact of neuroimmune interactions.
Chronic low back pain is a prime example of how neuroimmune dysfunction can sustain pain over time. The ongoing interaction between neurons, glial cells, and immune cells doesn’t just initiate pain – it maintains it for months or even years [4][5]. This persistent dialogue, often triggered by initial tissue damage, is a hallmark of chronic low back pain.
In conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, joint inflammation highlights the evolving relationship between the nervous and immune systems. During inflammation, immune cells flood the joint space, releasing cytokines that activate pain receptors. In turn, the nervous system releases neuropeptides that influence immune cell activity, creating a feedback loop. This loop can either support healing or contribute to further joint damage, depending on the balance of signals.
Understanding these processes is key to developing effective, evidence-based strategies for managing musculoskeletal pain.
Evidence-Based Treatments for Neuroimmune Modulation
Chiropractic Care and Neuroimmune Health
Spinal adjustments have been shown to influence biomarkers tied to neuroplasticity, inflammation, and stress, which helps explain their clinical effectiveness [8]. When the spine is properly aligned, communication between the brain and immune cells improves, creating a more efficient neural-immune connection [7]. This interaction is a two-way street: neural signals can either activate or suppress immune responses, while immune cells, through cytokines, impact the nervous system [9][10]. By enhancing spinal function, chiropractic care helps to lower inflammation and manage stress – two key factors in maintaining a strong immune system [7]. These spinal adjustments not only address the neuroimmune aspects of musculoskeletal issues but also lay the groundwork for therapies that further promote neuroimmune balance.
Additional Techniques at Portland Chiropractic Group
In addition to spinal adjustments, several other therapies are used to support neuroimmune health.
The Graston technique employs specialized tools to break down congested soft tissue and release fascial restrictions. This process reduces inflammation and enhances nerve function, helping to restore a healthy neuroimmune balance in areas of injury.
Dry needling focuses on trigger points to ease muscle tension and decrease inflammatory signals that contribute to heightened nerve sensitivity. By targeting these localized issues, dry needling disrupts the cycle of pain and inflammation that can overstimulate neuroimmune pathways.
Shockwave therapy uses acoustic waves to promote cellular repair and improve circulation. The increased blood flow it generates helps deliver essential nutrients to healing tissues while flushing out inflammatory waste products, aiding the body’s natural recovery.
Together, these therapies work alongside chiropractic adjustments to provide a well-rounded approach to neuroimmune health. They address both the nervous system’s role in how we perceive pain and the immune system’s role in controlling inflammation and tissue repair.
Practical Strategies for Clinicians and Patients
Treatment Approaches for Clinicians
With a deeper understanding of neuroimmune dynamics, clinicians can adopt targeted manual therapies and lifestyle-focused interventions to address inflammation and pain effectively. Techniques like high-velocity, low-amplitude thrusts (HVLAT) for spinal manipulation are particularly useful for improving nervous system function and reducing stress-driven inflammation [12][14]. For patients who may need gentler alternatives, low-velocity, low-amplitude cervical mobilizations offer similar benefits without the rapid thrusts [12][13]. Additionally, some practitioners employ high-velocity, low-amplitude distraction manipulation at the cervico-thoracic junction to influence key neuroimmune pathways [12][13]. These precise methods are designed to directly address neuroimmune responses, helping to reduce both inflammation and pain.
However, manual techniques alone may not address the full spectrum of musculoskeletal conditions. A team-based, interprofessional approach becomes essential, particularly when addressing the psychological stress that often accompanies these conditions [15]. Stress activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the sympathetic nervous system, which, in turn, signal the immune system and heighten inflammation [2]. Incorporating stress management protocols into treatment plans helps break this cycle, allowing clinicians to address both physical and emotional factors. This comprehensive approach empowers patients to actively participate in their own neuroimmune health.
Self-Care Tips for Patients
While clinicians focus on tailored treatment plans, patients can take an active role in their recovery through consistent self-care practices. Regular exercise plays a key role, as it increases anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10 and IL-4, which help alleviate pain [11]. Exercise also promotes the resolution of inflammation through omega-3–derived mediators, making it a vital component of managing musculoskeletal conditions [11].
Diet is another critical factor. Incorporating omega-3-rich foods – such as fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds – supports the production of compounds that help resolve inflammation [11]. For individuals with chronic musculoskeletal pain, neuroimmune sensitization can involve issues like extracellular matrix fibrosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and maladaptive immune responses [16]. While professional treatments target these underlying issues, maintaining an active lifestyle and managing stress effectively can create an environment that supports healing. By combining targeted exercises with an anti-inflammatory diet, patients can help restore the neuroimmune balance necessary for recovery.
sbb-itb-ed556b0
Exploring the Neuroimmune Interface and Future of Pain Management with Professor Mark Hutchinson
Conclusion: Understanding and Addressing Neuroimmune Interactions
After examining treatment strategies, it’s clear that a deeper understanding of neuroimmune interactions is essential for tackling chronic pain. The connection between the nervous and immune systems plays a central role in musculoskeletal health. When this balance is disrupted, it can drive inflammation, amplify pain sensitivity, and alter pain processing, contributing to conditions like fibromyalgia, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis [17]. This knowledge opens the door to treatments that go beyond simply masking pain [17].
The scale of the challenge is staggering. Chronic pain affects around 50 million adults in the U.S. (20.4%), with annual treatment costs estimated between $560 and $635 billion – a financial burden greater than that of cancer and heart disease combined [17]. Pain-related complaints account for up to 60% of emergency department visits, highlighting the urgent need for more effective solutions [17].
Addressing these neuroimmune pathways isn’t just about improving clinical outcomes – it’s also about reducing the economic strain. To achieve this, treatments must focus on neuroimmune interfaces and mediators such as cytokines, glial cells, macrophages, and nerve fibers [17]. Combining targeted therapies with lifestyle changes offers a path to restoring balance. As Caroline M. Sawicki and her colleagues explain:
"Understanding neuroimmune mechanisms that underlie pain and comorbid symptoms may yield novel therapeutic strategies that integrate a collaborative and interdisciplinary approach in the treatment of chronic pain" [2].
It’s also critical to recognize that biological, psychological, and social factors all influence neuroimmune health. By addressing these interconnected elements through personalized care, clinicians and patients can work together to reduce inflammation, restore balance, and promote true healing. This approach shifts the focus from merely managing symptoms to tackling the root causes of chronic pain.
FAQs
How do interactions between the nervous and immune systems cause chronic pain in musculoskeletal conditions?
Neuroimmune interactions are a key factor in chronic musculoskeletal pain, driving processes that intensify the body’s pain response. When the immune system releases substances like cytokines and other mediators, these chemicals can irritate pain-sensitive nerves (nociceptors) and activate glial cells in the nervous system. This chain reaction leads to neuroinflammation, which amplifies pain signals and increases the nervous system’s sensitivity over time.
This heightened sensitivity, referred to as peripheral and central sensitization, can cause pain to linger long after the initial injury or inflammation has healed. This insight underlines the need to address both the nervous and immune systems when developing effective strategies for managing chronic pain.
How can lifestyle changes help manage neuroimmune dysfunction in musculoskeletal conditions?
Lifestyle adjustments can significantly impact how neuroimmune dysfunction is managed and aid in recovery from musculoskeletal conditions. By focusing on elements like stress management, staying active, and eating well, you can help balance the interaction between the nervous and immune systems. This balance plays a key role in reducing inflammation and managing pain more effectively.
Simple steps like incorporating regular exercise, practicing stress-relief techniques such as mindfulness or yoga, and sticking to a balanced, nutrient-packed diet can make a big difference. These habits not only support the body’s natural healing process but also contribute to maintaining healthier muscles and joints over time.
How do chiropractic adjustments support neuroimmune health in musculoskeletal conditions?
Chiropractic adjustments play a role in supporting the connection between the nervous and immune systems. By helping to reduce nerve irritation and improve how the nervous system functions, these adjustments may encourage the release of neurotransmitters that influence immune cell activity in a positive way.
This interaction can also help lower inflammation and make pain receptors less sensitive, which may lead to pain relief and better healing. By targeting these neuroimmune connections, chiropractic care provides a natural way to manage musculoskeletal issues without relying on invasive methods.
Related Blog Posts
- Top Integrative Therapies for Chronic Pain
- Why Nerves Do Not Get “Pinched” but Rather Get Irritated Through Chemical and Inflammatory Ischemia.
- Effectiveness of Articular and Neural Mobilization for Managing Cervical Radicular Pain: A Systematic Review With Network Meta-Analysis
- Tendinopathy: The Interplay between Mechanical Stress, Inflammation, and Vascularity



Comments are closed